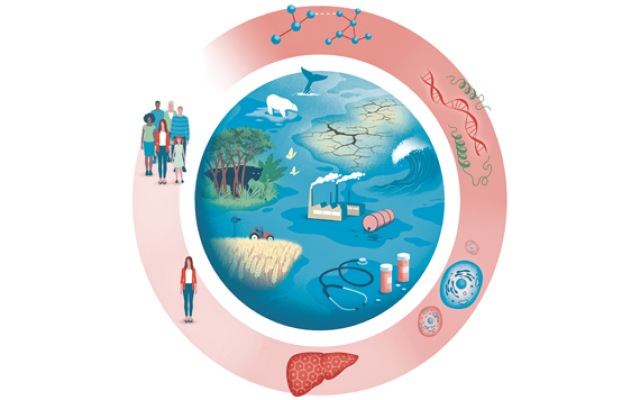
SIB Resources are used by millions of life scientists and clinicians around the world, with applications in health, food security and environmental protection. Browse this page for recent examples of how these 17 resources – together comprising 40 high-quality databases and software tools – accelerate discoveries and innovations that help address critical global issues.
Yearly impact of SIB Resources
12
million users
User definition and sources: Google Analytics, Plausible, Matomo
Search
Filter by
results